| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | WB, FC, IC |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal antibody |
| Gene Name: | major histocompatibility complex, class I, A |
| Gene Symbol: | HLA-A |
| Synonyms: | HLAA |
| Gene ID: | 3105 |
| UniProt ID: | P04439 |
| Clone ID: | 24GB6040 |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human MHC class 1 |
| Dilution: | WB 1:1,000-1:5,000; FC 1:2,000; IC 1:100-1:1,000 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purified |
| Concentration: | Lot dependent |
| Buffer: | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
Background
HLA-A belongs to the HLA class I heavy chain paralogues. This class I molecule is a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain and a light chain (beta-2 microglobulin). The heavy chain is anchored in the membrane. Class I molecules play a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from the endoplasmic reticulum lumen so that they can be recognized by cytotoxic T cells. They are expressed in nearly all cells. The heavy chain is approximately 45 kDa and its gene contains 8 exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the alpha1 and alpha2 domains, which both bind the peptide, exon 4 encodes the alpha3 domain, exon 5 encodes the transmembrane region, and exons 6 and 7 encode the cytoplasmic tail. Polymorphisms within exon 2 and exon 3 are responsible for the peptide binding specificity of each class one molecule. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. More than 6000 HLA-A alleles have been described. The HLA system plays an important role in the occurrence and outcome of infectious diseases, including those caused by the malaria parasite, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The structural spike and the nucleocapsid proteins of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), are reported to contain multiple Class I epitopes with predicted HLA restrictions. Individual HLA genetic variation may help explain different immune responses to a virus across a population.
Images
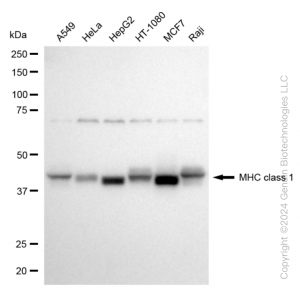
 | Western blotting analysis using anti-MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166). Total cell lysates (30 μg) from various cell lines were loaded and separated by SDS-PAGE. The blot was incubated with anti-MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166, 1:5,000) and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Cat#201, 1:20,000) respectively. Image was developed using NaQ™ ECL Substrate Kit (Cat#716). |
 | Western blotting analysis using anti-MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166). MHC class 1 expression in wild type (WT) and HLA-A shRNA knockdown (KD) HT-1080 cells with 20 μg of total cell lysates. Hsp90 α serves as a loading control. The blot was incubated with anti-MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166, 1:5,000) and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Cat#201, 1:20,000) respectively. Image was developed using anti-NaQ™ ECL Substrate Kit (Cat#716). HLA-A, Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class I. |
 | Flow cytometric analysis of MHC class 1 expression in HeLa cells using MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166, 1:2,000). Green, isotype control; red, MHC class 1. |
 | Immunocytochemical staining of HAP-1 cells with anti-MHC class 1 antibody (Cat#61166, 1:1,000). Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI; MHC class 1 was stained magenta with Alexa Fluor® 647. Images were taken using Leica stellaris 5. Protein abundance based on laser Intensity and smart gain:High . Scale bar, 20 μm. |
You may also be interested in: