| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | WB, FC, IC |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal antibody |
| Gene Name: | huntingtin |
| Gene Symbol: | HTT |
| Synonyms: | HD; IT15; LOMARS |
| Gene ID: | 3064 |
| UniProt ID: | P42858 |
| Clone ID: | 23GB6285 |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Huntingtin |
| Dilution: | WB 1:1,000-1:5,000; FC 1:2,000; IC 1:100-1:1,000 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purified |
| Concentration: | Lot dependent |
| Buffer: | PBS with 0.05% proclin300, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
Background
Huntingtin is a disease gene linked to Huntington's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. This is thought to be caused by an expanded, unstable trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene, which translates as a polyglutamine repeat in the protein product. A fairly broad range of trinucleotide repeats (9-35) has been identified in normal controls, and repeat numbers in excess of 40 have been described as pathological. The huntingtin locus is large, spanning 180 kb and consisting of 67 exons. The huntingtin gene is widely expressed and is required for normal development. It is expressed as 2 alternatively polyadenylated forms displaying different relative abundance in various fetal and adult tissues. The larger transcript is approximately 13.7 kb and is expressed predominantly in adult and fetal brain whereas the smaller transcript of approximately 10.3 kb is more widely expressed. The genetic defect leading to Huntington's disease may not necessarily eliminate transcription, but may confer a new property on the mRNA or alter the function of the protein. One candidate is the huntingtin-associated protein-1, highly expressed in brain, which has increased affinity for huntingtin protein with expanded polyglutamine repeats. This gene contains an upstream open reading frame in the 5' UTR that inhibits expression of the huntingtin gene product through translational repression.
Images
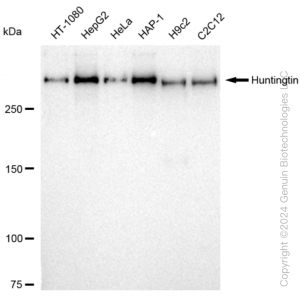
 | Western blotting analysis using anti-Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159). Total cell lysates (30 μg) from various cell lines were loaded and separated by SDS-PAGE. The blot was incubated with anti-Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159, 1:5,000) and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Cat#201, 1:20,000) respectively. Image was developed using FeQ™ ECL Substrate Kit (Cat#226). |
 | Western blotting analysis using anti-Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159). Huntingtin expression in wild type (WT) and Huntingtin shRNA knockdown (KD) HeLa cells with 20 μg of total cell lysates. Hsp90 α serves as a loading control. The blot was incubated with anti-Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159, 1:5,000) and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Cat#201, 1:20,000) respectively. Image was developed using NaQ™ ECL Substrate Kit (Cat#716). |
 | Flow cytometric analysis of Huntingtin expression in HepG2 cells using Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159, 1:2,000). Green, isotype control; red, Huntingtin. |
 | Immunocytochemical staining of HepG2 cells with anti-Huntingtin antibody (Cat#62159, 1:1,000). Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI;Huntingtin was stained magenta with Alexa Fluor® 647. Images were taken using Leica stellaris 5. Protein abundance based on laser Intensity and smart gain: Medium. Scale bar: 20 μm. |
You may also be interested in: